Site about Music - Art & Math


 The history of art is the history of any activity or product made by humans in a visual form for aesthetical or communicative purposes, expressing ideas, emotions or, in general, a worldview.( From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_art).
The history of art is the history of any activity or product made by humans in a visual form for aesthetical or communicative purposes, expressing ideas, emotions or, in general, a worldview.( From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_art).
The most important movements of art and architecture in European history are:
¤ Romanesque: Typical attributes of this style are painted walls, massive pillars, small round windows and doors, round arches, and later, carved doors.
Romanesque art refers to the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic style in the 13th century, or later, depending on region. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Romanesque_art)
¤ Gothic: It is known to be the highest and noblest of all styles. The main distinguishing features are rib vaulted ceilings, stone arches, and stained glass windows. The Notre Dame in Paris is built in this style.
Gothic art was a style of Medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, never quite effacing more classical styles in Italy.( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gothic_art)
¤ Renaissance: The word renaissance is representative of a period in which the role of townspeople increased and life on earth was celebrated. In Renaissance architecture, you can find lower buildings with simple facades ornamented by graffiti and stucco, horizontal lines, and square and rectangular windows and doorways. World famous artists of this period were Michelangelo Buonarotti and Leonardo da Vinci.
Renaissance art is the painting, sculpture and decorative arts of that period of European history known as the Renaissance, emerging as a distinct style in Italy in about 1400, in parallel with developments which occurred in philosophy, literature, music and science. ( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renaissance_art)
¤ Baroque: It was a period in which man turned back to God. Baroque art focuses on the themes of death, destitution, and starvation. The buildings of the time were based on classic models, full of splendor and nobility. Baroque architecture is known for luxury detail and extravagant decoration, such as curves, and ovals made of gold and marble. Also notable during this period was the play of contrast made between light and dark.
The Baroque (US /bəˈroʊk/ or UK /bəˈrɒk/) is often thought of as a period of artistic style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, architecture, literature, dance, and music. The style began around 1600 in Rome, Italy and spread to most of Europe. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baroque
¤ Rococo: The Rococo period is marked by elegance, lightness, and cheerful decoration. Paintings during this period returned to nature and the exotic, and often featured love scenes. Rococo (/rəˈkoʊkoʊ/ or /roʊkəˈkoʊ/), less commonly roccoco, or "Late Baroque", is an 18th-century artistic movement and style, affecting many aspects of the arts including painting, sculpture, architecture, interior design, decoration, literature, music, and theatre. It developed in the early 18th century in Paris, France as a reaction against the grandeur, symmetry, and strict regulations of the Baroque, especially of the Palace of Versailles. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rococo)
¤ Classicism: It was a period marked by emphasis on reason over emotions and drew its inspiration from classical antiquity. It featured straight lines, light colors, and little decoration. Classicism, in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for a classical period, classical antiquity in the Western tradition, as setting standards for taste which the classicists seek to emulate. The art of classicism typically seeks to be formal and restrained. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classicism
¤ Neo-Baroque, Neo-Gothic, and Neo-Renaissance: A revival of Baroque, Gothic, and Renaissance styles emerged during the 19th century. Many churches and public buildings were built, drawing inspiration on the styles of previous periods.
¤ Art nouveau: It was a period of new values and new rules in art. Interesting new materials were used, including glass and ceramics.
The Renaissance was a period of time from the 14th to the 17th century in Europe. This era bridged the time between the Middle Ages and modern times. The word "Renaissance" means "rebirth".

The word “Baroque” is the term used to describe Western art and architecture in the 17th century. The exact origins of the word are unclear.
Read the full story »
Rococo (/rəˈkoʊkoʊ/ or /roʊkəˈkoʊ/), less commonly roccoco, or "Late Baroque", is an 18th-century artistic movement and style, affecting many aspects of the arts including painting, sculpture, architecture, interior design, decoration, literature, music, and theatre.
Read the full story »
The term “Romanticism” encapsulates many and varied aspects. For Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778) Romanticism meant a return to nature; for Johann Wolfgang von Goethe ( 1749-1832) it was disease; for Heinrich Heine ( 1797-1856) it was the infinite; for Victor Hugo ( 1802-1885) the truth of life; for George Sand (1804-1876) the art of the emotions and of the heart; and for Charles Baudelaire ( 1821-1867) the modern.
Read the full story »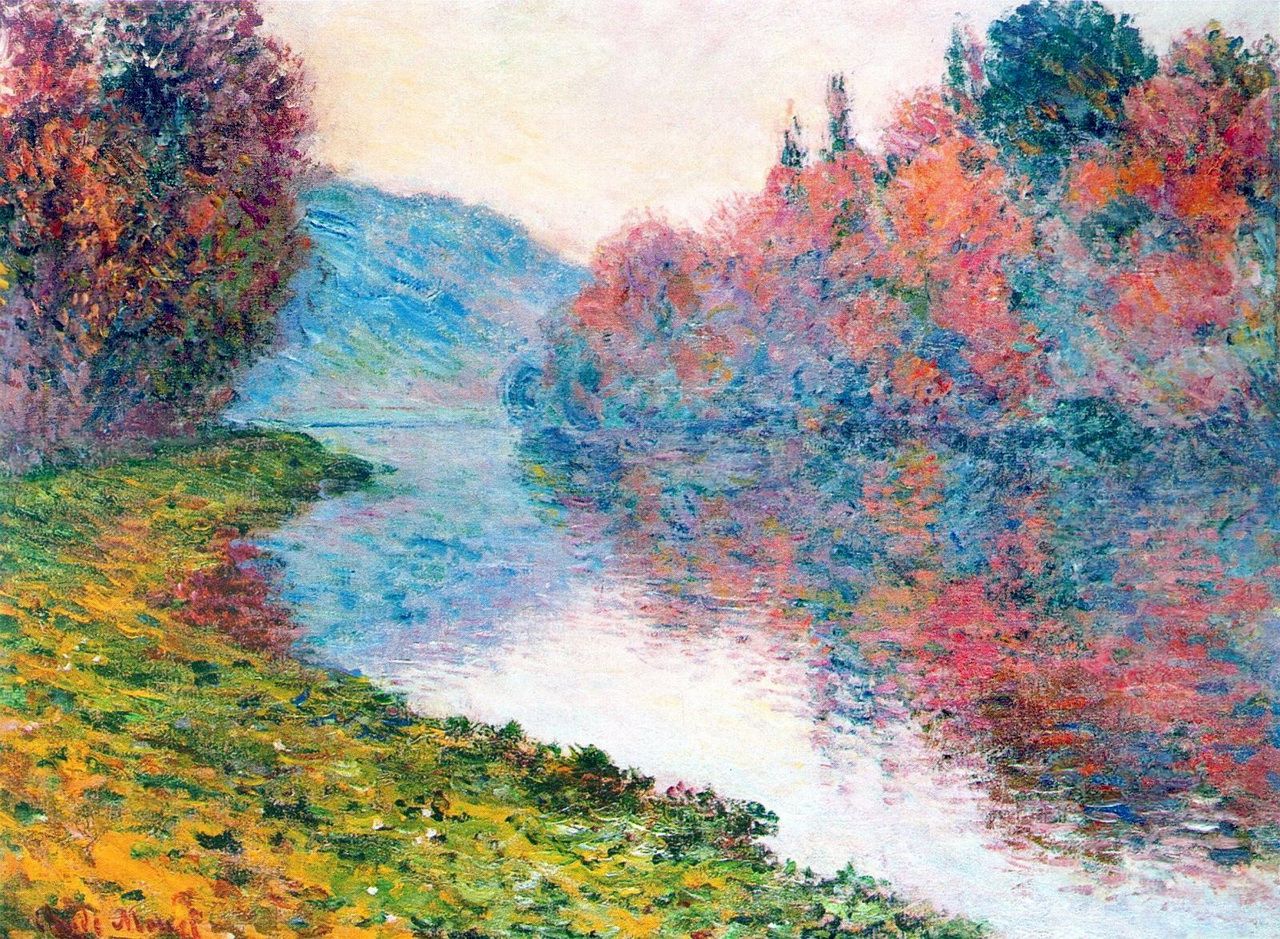
Impressionism is a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage of time), ordinary subject matter, inclusion of movement as a crucial element of human perception and experience, and unusual visual angles
Read the full story »